In an era where environmental sustainability is paramount, the automotive industry stands at the forefront of innovation, striving to minimize its carbon footprint. Among the most significant strides made are the advancements in decarbonization technologies. Central to these developments are three precious metals: silver, platinum, and palladium. These metals play a critical role in the transition to cleaner, greener automobiles.
Growing Regulation on Automobile Emissions
As the world becomes increasingly aware of the environmental impact of vehicle emissions, governments around the globe are implementing stringent regulations to curb pollution and promote cleaner transportation. Here are some key regulations in place across different regions:
Europe
Euro 6 Standards: The European Union has implemented Euro 6 standards, which set limits on emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and hydrocarbons (HC) from vehicles. These standards apply to all new vehicles sold in the EU since September 2015.
CO2 Emission Targets: The EU has set ambitious targets to reduce average CO2 emissions from new cars to 95 grams per kilometer by 2021, with further reductions planned for 2025 and 2030.
United States
Tier 3 Standards: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has introduced Tier 3 standards, which aim to reduce emissions of NOx, PM, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from passenger cars and light-duty trucks. These standards are set to be fully implemented by 2025.
California Air Resources Board (CARB): California has its own stringent emission standards, known as the California Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) program, which often sets the benchmark for other states in the U.S.
China
China 6 Standards: China has adopted the China 6 standards, which are similar to the Euro 6 standards and aim to reduce emissions of NOx, PM, and HC from vehicles. These standards are being phased in from 2020 to 2023.
New Energy Vehicle (NEV) Mandate: China has implemented a mandate requiring automakers to produce a certain percentage of new energy vehicles (NEVs), including electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids, to promote the adoption of cleaner vehicles.
Japan
Post-New Long-Term Emission Standards: Japan has introduced post-new long-term emission standards, which set limits on NOx, PM, and HC emissions from vehicles. These standards are part of Japan's efforts to achieve its greenhouse gas reduction targets.
Fuel Efficiency Standards: Japan also has stringent fuel efficiency standards, requiring automakers to improve the fuel economy of their vehicles.
India
Bharat Stage (BS) VI Standards: India has implemented the Bharat Stage VI (BS VI) standards, which are equivalent to the Euro 6 standards and aim to reduce emissions of NOx, PM, and HC from vehicles. These standards came into effect in April 2020.
Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) Standards: India has also introduced CAFE standards, which set targets for the average fuel efficiency of vehicles produced by automakers.
These regulations are part of a global effort to reduce vehicle emissions and mitigate the impact of transportation on the environment. By implementing and adhering to these standards, countries are working towards a cleaner and more sustainable future.
The Quest for Decarbonization
Decarbonization refers to the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions through various technological and regulatory measures. For the automotive sector, this means reducing emissions from vehicles, improving fuel efficiency, and ultimately transitioning to zero-emission vehicles such as electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs).
The Evolution of Vehicles
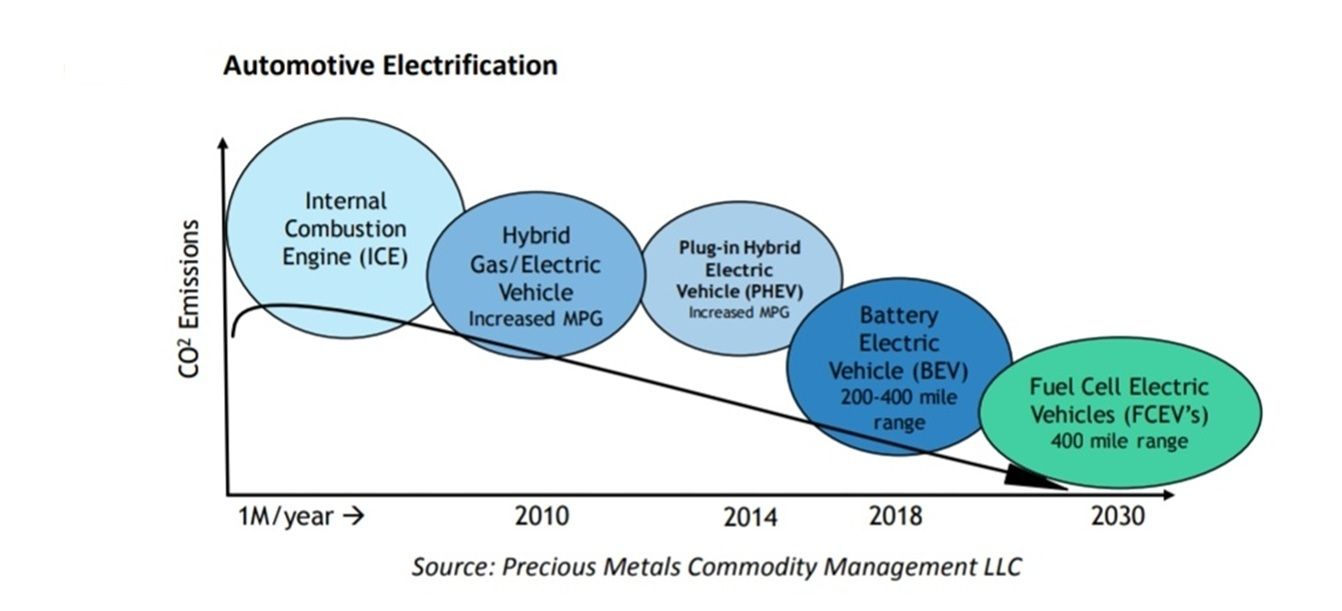
The automotive industry has been undergoing a significant transformation, moving from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to more sustainable alternatives. Here's a look at the different stages:
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles: Powered by gasoline or diesel, these vehicles have been the standard for over a century.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): These combine a conventional ICE with an electric propulsion system, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Similar to HEVs but with the ability to recharge their batteries by plugging into an external power source.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Fully electric vehicles that rely solely on battery power, producing zero tailpipe emissions.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): These use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, with water vapor as the only byproduct.
Silver: The Unsung Hero of EVs
Silver, known for its excellent conductivity, is indispensable in the manufacturing of electric vehicles. Its primary role is in the production of photovoltaic cells and various electrical components within EVs. Here’s why silver is so important at each stage:
ICE Vehicles: Silver's role is limited but still present in electrical components and contacts.
HEVs: The introduction of electric propulsion systems increases the need for silver in electrical components and battery systems.
PHEVs: The demand for silver grows further due to the need for efficient battery charging systems and connectors.
BEVs: Silver is crucial in the manufacturing of batteries, inverters, and charging stations, making these vehicles highly efficient.
FCEVs: Silver is used in fuel cell stacks and hydrogen production, contributing to the overall efficiency of these vehicles.
Platinum: The Catalyst for Clean Emissions
Platinum is at the heart of catalytic converters, which are essential for reducing harmful emissions from internal combustion engine vehicles. Catalytic converters transform toxic gases into less harmful substances before they are emitted from the exhaust. Here’s how platinum contributes:
Diesel Engines: Platinum is a key component in diesel particulate filters (DPFs) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, which reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from diesel engines.
Fuel Cells: In hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs), platinum is used as a catalyst to facilitate the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing electricity with water as the only byproduct.
Palladium: The Emissions Reducer
Like platinum, palladium plays a crucial role in catalytic converters, particularly for gasoline engines / petrol engines. Its ability to absorb and store hydrogen makes it invaluable in reducing emissions. Here’s why palladium is essential:
Catalytic Converters: Palladium helps in the oxidation of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, reducing the levels of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere.
Fuel Cells: Palladium is also used in hydrogen storage and fuel cells, similar to platinum, aiding in the production of clean energy for FCEVs.
The Synergy of Precious Metals in a Sustainable Future
As the automotive industry progresses towards a sustainable future, the roles of silver, platinum, and palladium will become even more pronounced. These metals not only contribute to the reduction of vehicle emissions but also enhance the efficiency and reliability of emerging technologies such as EVs and FCEVs. The continued innovation and application of these precious metals are essential for the realization of a low-carbon future.
Conclusion
The journey towards automobile decarbonization is complex and multifaceted, with silver, platinum, and palladium playing pivotal roles. Their unique properties and applications are driving the transformation of the automotive industry, paving the way for greener and more sustainable transportation solutions. As we look ahead, the continued development and integration of these metals will be crucial in achieving our environmental goals and ensuring a cleaner, healthier planet for future generations.
By embracing these advancements and supporting the use of precious metals, we can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable world and leave a lasting legacy for generations to come.
0 Comments